前言:在JavaScript中比较常见的创建对象的方式就是使用new操作符号配合构造函数的模式来创建对象,但是有没有想过new的时候构造函数都做了些什么事情,今天就来简单的看下!
new的原理
现在要创建一个新的对象,比如这个对象是一个人(Person),代码如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
|
function Person(name, age, job) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
this.job = job;
this.sayName = function () {
console.log(this.name);
};
}
let person1 = new Person("Walter White", 50, "Chemist");
|
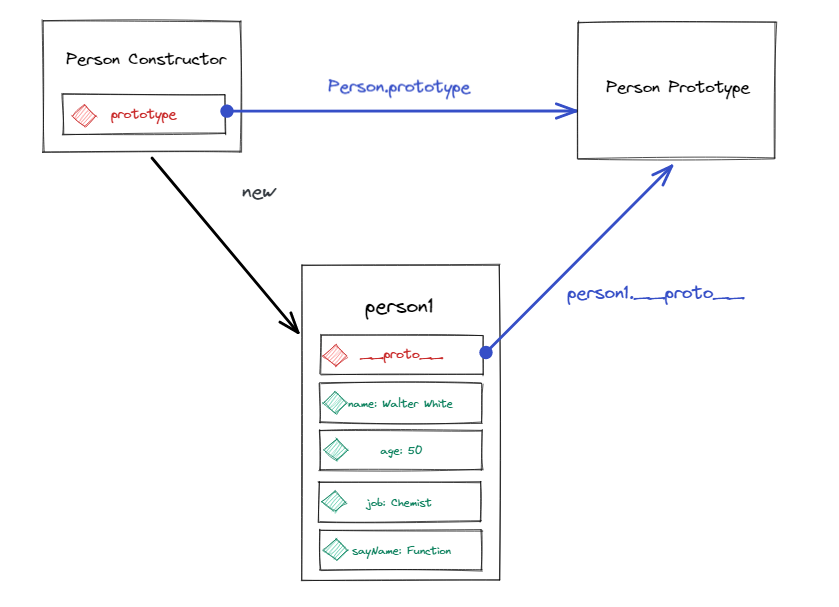
当使用new操作符的时候,进行以下操作:
- 在内存中创建一个新的对象
- 将这个对象的
__proto__指向构造函数的prototype(原型对象)
- 让
this指向这个新的对象
- 执行构造函数内部的代码,给这个对象添加属性与方法
- 返回这个新的对象(所以构造函数里面不需要写
reutrn)
下面来看下代码上的实现:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
|
function Person(name, age, job) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
this.job = job;
this.sayName = function () {
console.log(this.name);
};
}
function myNew(Class, ...args) {
// 1. 在内存中创建一个新的对象
const o = new Object();
// 2. 将这个对象的__proto__指向构造函数的prototype(原型对象)
o.__proto__ = Class.prototype;
// 3.让this指向这个对象
// 4.指向构造函数的代码,给这个对象添加属性与方法
const result = Class.call(o, ...args);
// 5.返回这个新对象
return typeof result === "object" ? result : o;
}
// 使用new创建
let person1 = new Person("Walter White", 50, "Chemist");
// 使用手写函数创建
let person2 = myNew(Person, "Walter White", 50, "Chemist");
console.log(person1); // Person {name: 'Walter White', age: 50, job: 'Chemist', sayName: ƒ}
console.log(person2); // Person {name: 'Walter White', age: 50, job: 'Chemist', sayName: ƒ}
|
补充
myNew函数优化写法:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
|
function myNew(Class, ...args) {
// 1. 在内存中创建一个新的对象
// 2. 将这个对象的__proto__指向构造函数的prototype(原型对象)
const obj = Object.create(Class.prototype);
// 3.让this指向这个对象
// 4.指向构造函数的代码,给这个对象添加属性与方法
let result = Class.apply(obj, [...args]);
// 5.返回这个新对象
return typeof result === "object" ? result : obj;
}
|
const obj = Object.create(Class.prototype);等价于
1
2
3
4
|
// 1. 在内存中创建一个新的对象
const o = new Object();
// 2. 将这个对象的__proto__指向构造函数的prototype(原型对象)
o.__proto__ = Class.prototype;
|
参考文献
